What is an atypical earache? While most people associate earaches with common issues like infections or fluid buildup, atypical earaches can present a unique set of challenges. These earaches often manifest in ways that are not easily attributed to standard causes, leading to confusion and concern for those affected. Atypical earaches may result from various underlying conditions, including dental issues, jaw problems, or even sinus infections. Understanding these atypical symptoms is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, we will explore what defines an atypical earache, its potential causes, and when it’s essential to seek professional help.
Key Takeaways
- Definition: An atypical earache refers to ear pain that arises from conditions outside of the ear, such as jaw issues, dental problems, or sinus infections, rather than from typical causes like ear infections.
- Causes: Common causes include Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) disorders, dental issues (e.g., cavities, impacted teeth), throat or neck infections, sinusitis, and nerve irritation near the ear.
- Symptoms: Unlike typical ear infections, atypical earaches may not involve fever, ear discharge, or hearing loss. Pain often radiates from the jaw, neck, or teeth, and may include tingling, jaw stiffness, or tooth sensitivity.
- Diagnosis: Atypical earaches are diagnosed by ruling out direct ear issues through physical exams, dental assessments, or imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. Specialists may be consulted to find the root cause.
- Treatment: Treatment targets the underlying issue and may involve jaw exercises, dental work, antibiotics for infections, or warm compresses for symptom relief.
- Prevention: Preventing atypical earaches includes managing stress, maintaining good oral hygiene, addressing posture issues, and treating sinus or jaw problems promptly.
Understanding Atypical Earaches
To fully understand the answer to "what is an atypical earache", we need to first explore how it differs from a regular earache. Traditional ear pain often results from issues like ear infections or blockages within the ear. However, atypical earaches can originate from other areas close to the ear, such as the jaw, throat, neck, or sinuses.
In these cases, the pain you feel in your ear might actually be a result of nerve signals from other parts of your body, leading to "referred pain." This makes diagnosing an atypical earache more challenging, as the underlying cause might not immediately be apparent. Understanding what makes an earache atypical can be key to proper treatment and relief.
What Causes an Atypical Earache?
If you’re asking yourself, what is an atypical earache, you’re likely wondering what causes this unusual form of ear pain. Atypical earaches can be caused by a wide variety of factors that aren't directly related to ear health. The proximity of the ear to other structures like the jaw, throat, and neck means that issues in these areas can manifest as ear pain.
Common causes of an atypical earache include problems with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), dental issues, infections in the neck or throat, and sinus problems. Sometimes, nerve irritation is the culprit, causing pain that is perceived in the ear but originates elsewhere in the body. Knowing these causes can help you better understand what an atypical earache is and how to address it.
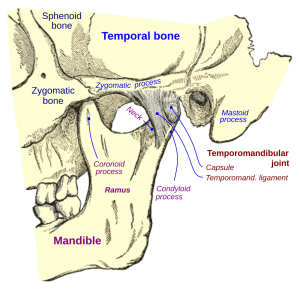
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
One of the leading causes of atypical ear pain is a problem with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). The TMJ is the joint that connects your jaw to your skull, and it sits very close to the ears. When this joint becomes inflamed or misaligned, it can lead to pain that is felt in the ear even though the ear itself is perfectly healthy. TMJ disorders are a common explanation when people ask, what is an atypical earache. Conditions like teeth grinding, jaw clenching, or arthritis in the joint can all contribute to this pain, which can be persistent and quite uncomfortable.
Dental Problems
Another frequent cause of atypical earaches comes from dental issues. People often don't realize that tooth pain can radiate to the ears. Problems like impacted wisdom teeth, cavities, or gum infections can cause referred pain, making it feel like your ear is the source of discomfort. This often leads people to ask, what is an atypical earache, especially when no ear infection is found. The complex network of nerves connecting your teeth, jaw, and ears means that dental issues can easily cause ear pain. If you've recently experienced a toothache along with ear pain, it's possible that your earache is atypical and related to a dental condition.
Neck and Throat Infections
Neck and throat infections can also be responsible for atypical ear pain. When you have a sore throat or conditions like tonsillitis, the nerves in your throat and neck can become irritated, and this irritation can cause pain that is felt in the ear. This type of referred pain is another example of what an atypical earache can be. Infections in the neck or throat don't directly impact the ear, but because the ear, throat, and neck share nerve pathways, pain in one area can easily be perceived in the other. If you’re suffering from a throat infection and your ears hurt, it’s likely an atypical earache.
Sinusitis
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, can often cause pressure and pain throughout the head, including the ears. The buildup of fluid and inflammation in the sinus cavities creates pressure that can affect the surrounding areas, including the ears. This is another common reason people experience atypical earaches. If you’ve ever had a cold or sinus infection and noticed that your ears also feel sore or pressured, you’ve likely had an atypical earache. The good news is that treating the underlying sinus issue often alleviates the ear pain as well, but it’s important to understand that what is an atypical earache in this case is related to sinus congestion, not an ear infection.
Ear Nerve Irritation
Another potential cause of an atypical earache is nerve irritation. Several nerves, such as the glossopharyngeal and trigeminal nerves, are involved in transmitting sensation to the ear. If these nerves become irritated or inflamed, the pain can manifest as an earache, even though the ear itself might be completely healthy. This is why people often ask, what is an atypical earache, especially when there’s no obvious cause. Nerve irritation can be caused by many factors, including injury, inflammation, or even stress. If the pain feels sharp, tingling, or radiating, it might be due to nerve involvement.
Recognizing the Symptoms of an Atypical Earache
Recognizing the symptoms of an atypical earache can help differentiate it from a traditional ear infection. While typical earaches often come with symptoms such as ear discharge, hearing loss, or fever, what is an atypical earache is a different story. Atypical earaches are less likely to involve those traditional signs and more likely to come with pain that radiates from other areas like the jaw, neck, or teeth. You might experience jaw stiffness or soreness, neck pain, or even tooth sensitivity alongside the ear pain.
Additionally, atypical earaches don’t usually come with fever, which is a common sign of a typical ear infection. Understanding these symptoms is crucial to determining whether the earache is truly atypical.
Diagnosing an Atypical Earache
To diagnose what is an atypical earache, your healthcare provider will first need to rule out any direct ear-related issues. This often starts with a physical examination of the ear, throat, jaw, and neck to check for any visible signs of infection or injury. If no direct ear problems are found, your doctor may investigate other possible causes, such as TMJ disorders or dental issues. Imaging tests, like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, may also be recommended to get a closer look at areas like the jaw or sinuses.
In some cases, you might be referred to a specialist such as a dentist, orthodontist, or neurologist, depending on what the suspected underlying cause might be. Diagnosing an atypical earache is often a process of elimination, where your healthcare provider will work to uncover the true source of your pain.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is usually the first step in diagnosing what is an atypical earache. During the exam, your doctor will check your ears, neck, jaw, and throat for any signs of infection, injury, or inflammation. This helps rule out more common causes of ear pain and provides clues about whether the pain is referred from another area. In many cases, the physical exam alone can give doctors a good indication of whether you're dealing with an atypical earache or something more standard like an ear infection. If the exam points to an issue outside the ear, further tests might be ordered.
Imaging Tests
If the cause of the earache isn’t obvious from the physical exam, imaging tests may be necessary to pinpoint the issue. X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs are often used to look for abnormalities in the jaw, neck, or sinuses that might be causing referred pain. For example, if a TMJ disorder is suspected, an X-ray can show any misalignment or damage in the jaw joint that could be contributing to what is an atypical earache. Imaging is particularly useful when the source of pain is hidden deep within the jaw, neck, or sinus cavities, making it easier to diagnose and treat the problem.
Dental Assessment
In cases where dental problems are suspected to be the cause of an atypical earache, a referral to a dentist or orthodontist might be necessary. Dental X-rays can reveal issues like impacted wisdom teeth, cavities, or infections that could be causing the pain to radiate to the ears. Often, people who ask, what is an atypical earache, are surprised to learn that their ear pain is related to a dental condition. A dental assessment can help confirm whether a tooth or gum problem is the underlying cause, and once treated, the earache typically resolves.
Treatment Options for Atypical Earaches
Treating an atypical earache depends entirely on the underlying cause of the pain. Since an atypical earache often stems from issues unrelated to the ear itself, treatment is aimed at addressing the root problem, whether it's a jaw disorder, a dental issue, or a sinus infection. Understanding what is an atypical earache means knowing that it might require treatment from a variety of healthcare professionals, such as a dentist, orthodontist, or ENT specialist. For example, if TMJ disorder is the culprit, treatment might involve jaw exercises, pain relief medication, or even a custom-fitted mouthguard. If a dental problem is to blame, a filling, extraction, or other dental work might be needed.
TMJ Disorder Treatment
When TMJ disorders are the cause of an atypical earache, treatment focuses on relieving tension and inflammation in the jaw joint. Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and jaw exercises are commonly recommended. In some cases, a mouthguard might be prescribed to prevent teeth grinding, especially if that is contributing to the problem. For more severe TMJ disorders, additional treatments such as physical therapy or even surgery might be necessary. Understanding what is an atypical earache caused by TMJ means knowing that the key to relief lies in addressing the jaw, not the ear.
Dental Treatment
If a dental issue is behind your atypical earache, treatment will focus on resolving the tooth or gum problem that is causing the referred pain. This could involve anything from filling a cavity to extracting a problematic tooth. Antibiotics may also be prescribed if there is an infection present. People often discover what is an atypical earache after visiting a dentist for an earache that has no clear ear-related cause. Once the dental issue is treated, the ear pain often disappears.
Treating Infections
When sinus or throat infections are responsible for atypical earaches, treatment involves reducing the inflammation and pressure that is causing the pain. This often includes antibiotics, antivirals, or over-the-counter decongestants. For sinus-related atypical earaches, nasal sprays or antihistamines might be recommended to clear up congestion and reduce pressure. Understanding what an atypical earache in the context of infections is means recognizing that the root cause is not in the ear, but in the sinuses or throat.
Preventing Atypical Earaches
Preventing an atypical earache involves managing the underlying conditions that cause referred ear pain. If you frequently suffer from atypical earaches, it’s important to take proactive steps to maintain overall health in areas that can contribute to ear pain, such as the jaw, teeth, and sinuses. Understanding what is an atypical earache means knowing that prevention starts with addressing issues outside of the ear itself.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Keeping your teeth and gums healthy can prevent dental-related earaches. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can catch problems before they escalate into referred pain.
- Manage Stress: Stress is a major contributor to TMJ disorders, which are a common cause of atypical earaches. Incorporating relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce tension in the jaw and prevent pain.
- Address Posture Issues: Poor posture, especially while sitting for long periods, can lead to neck and jaw problems that cause referred ear pain. Make a conscious effort to maintain good posture throughout the day to prevent neck strain that could contribute to what is an atypical earache.
When to See a Doctor for an Atypical Earache
While some earaches resolve on their own, atypical earaches often require medical intervention, especially if the pain persists for an extended period or if other symptoms accompany the pain. If you’re wondering what is an atypical earache and when to seek help, consider these factors:
- The pain lasts more than a few days: If your ear pain doesn’t improve or worsens over time, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
- You experience additional symptoms: Severe headaches, dizziness, or facial numbness in conjunction with ear pain could indicate a more serious issue and should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Your daily activities are affected: If the earache is impacting your ability to carry out normal activities, such as eating, sleeping, or concentrating, it’s time to seek medical advice.
Find Relief with Raleigh Facial Pain: Understanding Atypical Earaches
Raleigh Facial Pain specializes in diagnosing and treating atypical earaches, offering tailored solutions to alleviate discomfort and address the root causes. Our experienced team utilizes advanced techniques to provide comprehensive care that can significantly improve your quality of life.
If you're experiencing an atypical earache, don’t hesitate to reach out to Raleigh Facial Pain for expert assistance. Your path to relief starts here!