Typical treatment for toothache is root canal ? Inside nerve removed
If inside nerve was cause pain, pain would go away with root canal ? Yes
What does that tell you about cause pain ? not inside nerve
1) Inside nerves
2) Outside nerves
1) 2nd opinion (2 brains better one)
1) Retest inside nerve
2) Even they have difficult choices depending on interpreting data
a) Performs 2nd root canal
b) Refers orofacial pain specialist
An endodontist will refer Orofacial Specialist on any tooth that does not have conclusive evidence on inside nerve
2) 2nd opinion (2 brains better one)
3) Test outside nerve
4) Manage outside nerve
5) Pain goes away
Have a few of them, are you convinced: you grind & clench.
Atypical toothache is one most expensive pathologies to diagnose and treat in todays dentistry. Chasing the pain ghost can take decades of dental reconstruction and can cost as much as small house. After root canal, retreat root canal, then extraction, then implant, then implant removal and you still have pain. This is close to being an epidemic proportion. The better choice would been second opinion by Orofacial Pain Specialist. An ole saying, Measure twice cut once!
Root Canal does not relieve excruciating pain of toothache ?
If inside nerve caused pain, root canal would have reduced pain
What does that tell you about cause pain ?
It is not from inside nerve
We need more information to understand real source pain:
Damage muscle refers to area of teeth
1) Muscles damage = trigger point
2) Trigger points refer pain to teeth:
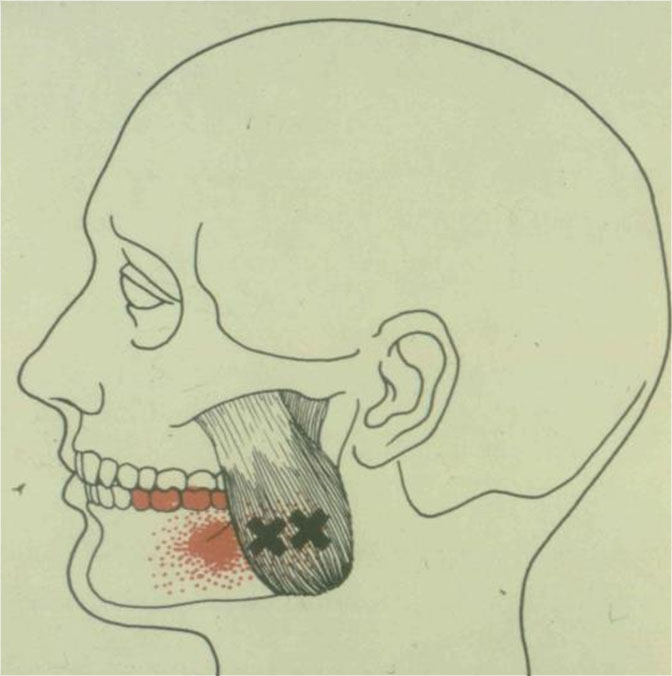
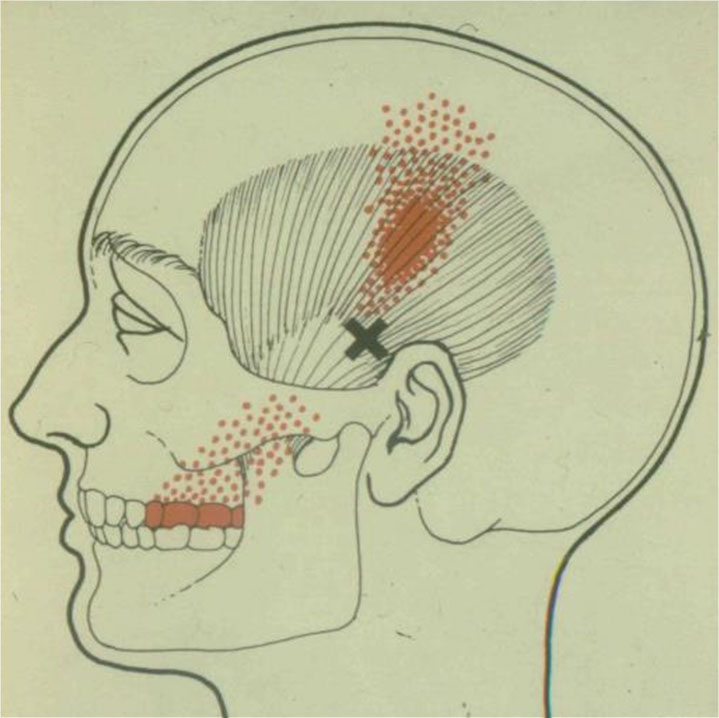
a) Masseter refers lower molars
b) Temporalis refers upper molars
Hints the Atypical toothache is not inside nerve
Excessive demands on chewing muscles:
1) Clench Grind
2) Tension Muscles
3) Guarding
4) Protective reflex
5) Habits
6) Chewing
7) Talking
8) Gum
| Muscle | Pulpal | |
| Type | Dull Ache | Sharp shooting |
| Severity | Mild to Mod | Mod to Severe |
| Location | Quadrant | Specific tooth |
| Aggravate | Chew Function | Biting tooth |
| Specificity | General | One tooth |
Text Book: Trigger Point Manual written by Dr. Janet Travell Headache in Pelvis by Wise & Anderson
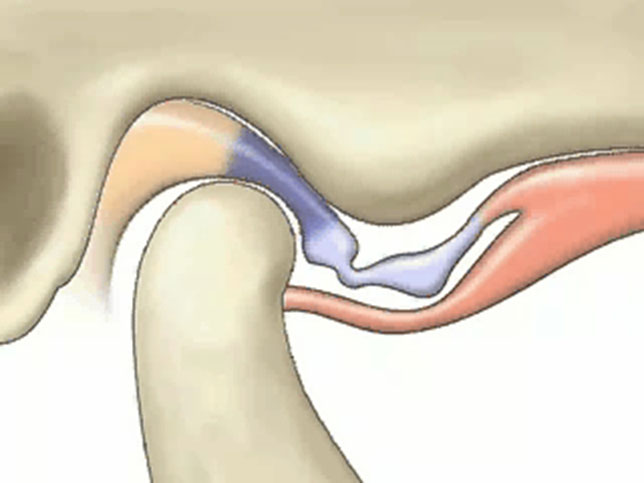
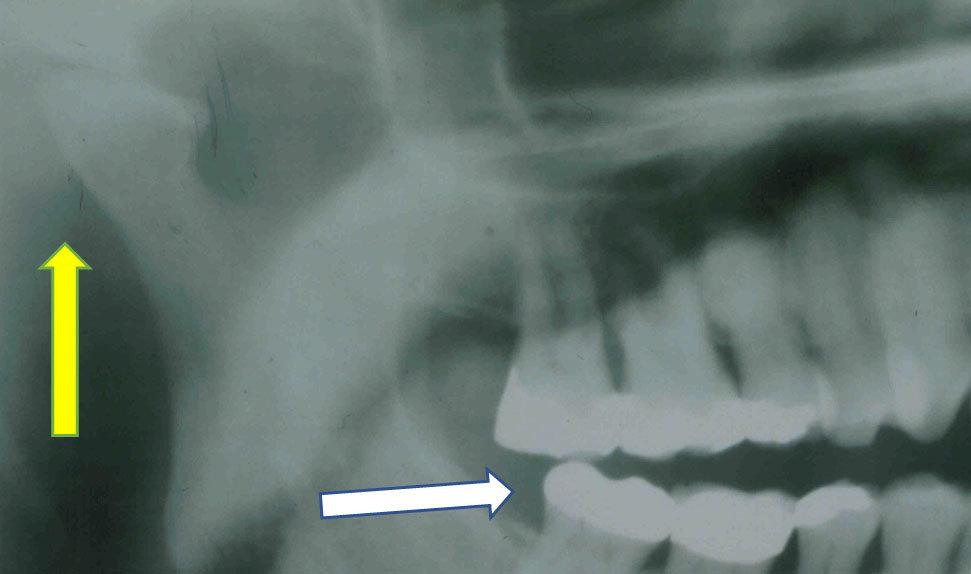
Your toothache is caused by excessive loading of posterior teeth due lost space in joint.
1) Sudden disc displacement
2) Bone loss in condyle
Refer orofacial pain = outside nerve specialist
1) Trigeminal Neuralgia
2) Atypical Odontalgia
3) Misc-sinus, heart, cancer, MS, Pagets
Trigeminal Neuralgia-5th nerve has a trigger near teeth
Atypical Odontalgia -neurovascular pathology of teeth
Miscellaneous (Sinus, tumor, MS, heart attack, Pagets)
Typical treatment for toothache is root canal ? Inside nerve removed
If inside nerve was cause pain, pain would go away with root canal ? Yes
What does that tell you about cause pain ? not inside nerve
1) Inside nerves
2) Outside nerves
1) 2nd opinion (2 brains better one)
1) Retest inside nerve
2) Even they have difficult choices depending on interpreting data
a) Performs 2nd root canal
b) Refers orofacial pain specialist
An endodontist will refer Orofacial Specialist on any tooth that does not have conclusive evidence on inside nerve
2) 2nd opinion (2 brains better one)
3) Test outside nerve
4) Manage outside nerve
5) Pain goes away
Have a few of them, are you convinced: you grind & clench.
Atypical toothache is one most expensive pathologies to diagnose and treat in todays dentistry. Chasing the pain ghost can take decades of dental reconstruction and can cost as much as small house. After root canal, retreat root canal, then extraction, then implant, then implant removal and you still have pain. This is close to being an epidemic proportion. The better choice would been second opinion by Orofacial Pain Specialist. An ole saying, Measure twice cut once!
Root Canal does not relieve excruciating pain of toothache ?
If inside nerve caused pain, root canal would have reduced pain
What does that tell you about cause pain ?
It is not from inside nerve
We need more information to understand real source pain:
Damage muscle refers to area of teeth
1) Muscles damage = trigger point
2) Trigger points refer pain to teeth:
a) Masseter refers lower molars
b) Temporalis refers upper molars


Hints the Atypical toothache is not inside nerve
Excessive demands on chewing muscles:
1) Clench Grind
2) Tension Muscles
3) Guarding
4) Protective reflex
5) Habits
6) Chewing
7) Talking
8) Gum
| Muscle | Pulpal | |
| Type | Dull Ache | Sharp shooting |
| Severity | Mild to Mod | Mod to Severe |
| Location | Quadrant | Specific tooth |
| Aggravate | Chew Function | Biting tooth |
| Specificity | General | One tooth |
Text Book: Trigger Point Manual written by Dr. Janet Travell Headache in Pelvis by Wise & Anderson
Your toothache is caused by excessive loading of posterior teeth due lost space in joint.
1) Sudden disc displacement
2) Bone loss in condyle


Refer orofacial pain = outside nerve specialist
1) Trigeminal Neuralgia
2) Atypical Odontalgia
3) Misc-sinus, heart, cancer, MS, Pagets
Trigeminal Neuralgia-5th nerve has a trigger near teeth
Atypical Odontalgia -neurovascular pathology of teeth
Miscellaneous (Sinus, tumor, MS, heart attack, Pagets)
a) soft biteguard: increase grinding, bulky, decrease airway space
b) soft-hard guards (Hybrids): increase clench, can’t…
 Raleigh Facial Pain © 2025 All Rights Reserved.
Raleigh Facial Pain © 2025 All Rights Reserved.