TMD Research:
- 30 yrs ago, dentistry studied teeth as only cause
- 20 yr ago, studies revealed causes were joint, muscle, & disc related
- 10 yrs ago, science indicated TMD was orthopedic science
Tearing Lateral Ligament-TMD Disc
- Primary Damaged:
- Clenching/grinding
- Tension muscles
- Trauma-MVA, Falls, Blows
- Neighboring pains (head & neck pain)
- Secondary damage:
- dual bites
- pain system escalation
- malocclusion
- open lock
CONFUSION TERMS in TMD World:
- TMD=name of joint not disease,
- TMD=broad collection structural damage all tissues chewing system
- Internal Derangement= structural damage to TMD
- Articular Disc Displacement = pathologies specific to disc
- Relationship disc to condyle: mild----moderate----severe
Relationship disc to condyle
- Mild =Partial Displaced Disc
- Moderate = Completed Disc Displacement
- Severe = Osteoarthritis
Mild disc displacement
- Includes: Muscle discomfort & partial disc displacement
- General dentist should treat or try prevent further damage
- Dentist needs to study this area of health for their patients
- Repeated recommendations prevent joint muscle damage
- Tooth damage we can treat but joint muscle damage is difficult treat
- Early mentioning of grind-clench makes appliances easier prescribe
- Early recognition of accumulative damage to all 4 chewing structure
- Early referral to OFPS in saga of atypical toothache reduces damage chewing structures
- Early recognition of anxiety issues coupled w/ TMD issues makes refer easier
- Recognition of accumulative trauma creates need for better history base
Moderate damage = need for referral to Orofacial Pain Specialist:
- Moderate chewing pain
- Restricted opening
- Referred ear pain
- Deviation opening
- Facial asymmetry
- Comorbid: Hypermobility, IBS, Sleep, Allergies, Sinus,
- High anxiety, need dental sedation, fear dentistry, PTSD, OCD, Bipolar
- Clenching & grinding
- Neighboring pains: neck and headache
- Atypical Toothache
- Burning mouth
- Trigeminal nerve injury
- Atypical earache
- Sleep apnea & TMD
Four primary factors
- Destructive Clench-Grind ( higher level grinding)
- Significant Tension muscles (back, neck, jaw, head)
- Trauma (MVA, Blows, Falls)
- Head & Neck pain (jaw muscle bracing due pain in neck or head)
Four secondary factors
- Open lock (subluxation TMD)
- Pain System Escalation
- Dual Bite (jaw jt bite vs tooth bite)
- Major Occlusal interferences-bite discrepancies
Tearing Lateral Ligament: assume 10, 000 fibers
- Age 12-26: habit clench/ grind tears 2 fibers per week = 1248 fiber
- Age 12-26: high muscle tension tears 1 fiber per week = 624 fibers
- Total Para tears (1248) + Tension tears (624) = total 1872
- MVA: moderate speed 25 mph: age 26 = tearing 828 fibers
- Age 26 to 36, habit clench/grind tears 4 fibers per week = 2496 fibers.
- Ager 26 to 36, tension in muscles tears 2 fibers per week =1248 fibers.
- Total Para tear (2496) + Ten tear (1248) = total 3744
- Total tearing by parafunction & tension muscles & MVA: 6444
- By age 36, She has torn over half of fibers of lateral ligament of TMD & has complete displace disc
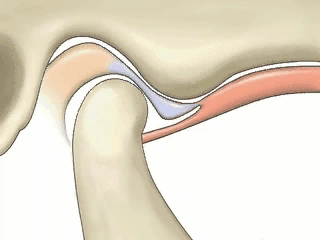
 Normal Position Disc
Normal Position Disc Displaced Disc
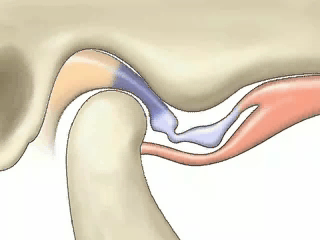
Displaced Disc Lateral Condylar Ligament Tearing
Lateral Condylar Ligament TearingTEARING LATERAL LIGAMENT A) MAJOR (TENSION, GRIND-CLENCH, TRAUMA, NEIGHBOR PAINS) B. MINOR: (OPEN LOCK, DUAL BITE, OCCLUSION, PAIN SENSITIZATION)
Destructive Clench/Grind:
Three levels grinding/clenching
- Mild
- Moderate
- Destructive
Symptoms destructive clench-grind
- Tooth movement after ortho
- Recession/bone loss
- Cracks-Broken fillings, teeth, crowns, bridges
- Loose implants
- Broken, cracked, chipped appliances
- Worn out dentition
- Failed implants
- Broken retainers, brackets, spacers
- Atypical toothace
- Atypical earache
- Cervical erosion
- Enlarging tori, bone buttressing
- Loose crown or bridges
- Build-ups broken off inside crown
- Tooth pain after cementation crowns
- Worn out night guards-biteguards in short time
Grinding/Clenching:
- Daytime: clenching, posturing, bracing, gnashing, nail biting, tongue biting, cheek biting, lip biting
- Nighttime grinding is more destructive due power at night exceeds the chewing power by 6 times.
- Need to measure power, frequency, and duration to determine damage potential
- Sleep studies measure breathing, sleep architecture, and grinding activity (only source data)
- Clenching & grinding damage all structures of chewing system: TEETH, BONE, MUSCLE, JOINT
Tension in Muscles
Three processes occur from anxiety/stress:
- CORTISOL
- ADRENALIN
- TENSION MUSCLES
Levels of tension in muscles:
- STRESS
- ANXIETY
- EMOTIONAL HYJACKING
- PTSD
Muscle Joint Pain is #2 pain world:
- BACK
- NECK
- HEAD
- JAW
Tension in Muscle Pathway:
Stress---Sympathetic---Gamma Efferent--Muscle spindle-- Tr Pt --Muscle Inflammation--PAIN
Ligament Tear:
Stress- Sympathetic-Lat Pterygoid-Pulls Lateral Ligament-Stretch-Tear Lat Lig- Disc Disp--PAIN
Progression Tearing:
Displace Disc Pathway: starts at lateral pole and proceeds to medial pole unless dentists intervenes
Lateral pole -- middle disc -- medial pole
Trauma
Traumas:
- BLOW
- MVA
- FALLS
- SPORTS INJURIES
WHIPLASH-MVA
- Lateral ligament of disc gets damaged
- Since ER does not pay attention to jaw joint in MVA's
- Cervical injuries are less image in ER today
- Request Cervical & TMD imaging if major MVA
- In one study 22 out 25 TMD's had displace disc after MVA
- Neck joints are same kind joint as in TMD
BLOWS-SPORT INJURIES:
- Sports injuries can causes sudden acceleration deaccleration of TMD
- Tearing of lateral ligament of disc of TMD
- Request imaging if limited opening or severe pain in TMD
- Record any symptoms TMD within months of Blow-Fall
- Blows to jaw typically damage the opposite TMD
- When mandible is not fracture, then maybe breaking TMD or major tearing lateral ligament
Sports-Related Injuries & TMD
- 11-18% all sports-related injuries were maxillofacial injuries
- 44-99% of TMD problems are caused by trauma
- Risk of sport-related female basketball injury rate = 7.5%
- 600,000 sports related visits to ER for craniofacial injuries

HEAD & NECK PAIN
Neck Pain: Neighboring Pains:
- Two types contraction:
- Muscle bracing: brace jaw muscles to contract neck muscles
- Muscle guarding: Pain causes muscles to protect & guard
- 3 layers neck muscles (outside, intermediate, intercostal)
- Added to muscle contraction:
- head movement
- muscle tension
- work posture
- muscle brace
- trigger points
- weight head or shoulders
- posture
- shrugging
- Cervical muscle bracing stimulates jaw clenching, jaw clenching contracts neck muscles
Head Pain: Neighboring Pains:
- Added muscle contraction due headache
- Muscle bracing
- Muscle guarding
- Primary Types HA:
- Tension Headaches
- Migraines
- Migraine Pain: sources inflammation
- Chewing muscles & joints
- Neck muscles & joints
- Special organs: ears, nose, sinus, mouth
- Virus & Bacteria
- Allergies, chemical sensitivities, hypermobility
- Tension Headache
- Stress sets off biochemical pathway: i) cortisol, ii) adrenalin, iii) tension
- Stress causes static muscle contraction of our favorite muscle
- Pathway: Stress-sympathetic system-temple contraction-lactic acid buildup-inflammation-pain
- Tension headache pain is mostly felt in temples
- Temple muscle is chewing muscle
- 48% women & 38% men have tension HA
Pain System Escalation
- Increasing Pain signals:
- Trauma Injury-Muscle bracing protect joint
- Grinding/clenching
- Anxiety wires to pain system
- Normal Jaw Joint function
- Decrease in pain inhibitory system
- Change in pain neurotransmitters
- Other Biochemical & physiological changes
- Pain system changes:
- length each pain,
- intensity pain,
- pain from nonpainful stimulus,
- wider area pain,
- perception pain
- Poor health habits decrease chance of healing; thus, a likely perpetuation of pain
- Pain itself causes increase in muscle contraction in certain muscle groups (back, neck, head, jaw)
Open Lock
- True subluxation TMD
- Condyle comes out of the socket
- Causes microtearing lateral ligament w/ each open lock
- Cause macrotearing if you try force it closed
- Only 2% of 6% population can even accomplish open lock, hypermobility
- Requires: a) anterior slope eminence, b) completely displaced disc
- Stretching then tearing sets up progressive tearing lateral ligament
- Severely torn lateral ligament causes complete displace disc
- Open lock tear adds to grind/clench-tension muscle-Trauma tearing-Neighoring pains
Dual Bite
- Difference between jaw joint bite and tooth bite
- Teeth control muscles to protect teeth
- Jaw joint wants power control muscles to full seat joint-relax muscles
- Definitions:
- Tooth bite is maximum interdigitation teeth
- Jaw joint bite is fully seated condyles in fossa
- Control of chewing muscles = “muscle guarding”
- Teeth controll muscles to go into tooth proctected bite
- Jaw joint tries order muscles to allow fully seated condyles
- There are teeth in way to full seat condyles
- So conflict erupts between muscle controlls
- This muscle guarding by both controllers increases muscle inflammation
- Muscle overuse or over contraction contributors
- Joint laxity = hypermobility = dual bite
- Tooth position does not allow full seat joint
- Orthotic allows full seat jaw joint w/o teeth interfering w/ the jaw joint need fully seat
- Who has dual bite?
- 85 % no dual bite
- 10 % small dual bite
- 5% moderate dual bite
- Great difference Dual Bite, the greater muscle activity
 Jaw joint Bite
Jaw joint BiteInterferences/Occlusal issues
- Interferences are contact of teeth by sides of cusps that interfere w/ cusp/fossa contact
- Interferences activate more muscle activity to try to avoid them
- Interferences are not powerful enough by themselves to cause much muscle/joint damage
- Grinding/clenching is power behind damage attributed to an interference
- Disclusion of posterior teeth by anterior guidance reduces activity of Temporalis & Masseter, 1983 J Pros






 Raleigh Facial Pain © 2026 All Rights Reserved.
Raleigh Facial Pain © 2026 All Rights Reserved.